The Role of Protein in a Balanced Daily Diet: What You Need to Know

Proteins are an essential component of a balanced diet and play a vital role in maintaining a healthy body. They are responsible for repairing and building cells, supporting growth and development, and contributing to overall well-being. Understanding the importance of protein and incorporating it into your daily nutrition can significantly impact your health.
Consuming a balanced diet that includes an adequate of protein is crucial for healthy eating and nutrition. Itc is made up of amino acids, which are essential for the body to function properly. While meat, fish, and eggs are excellent sources of protein, plant-based options like legumes, nuts, and seeds also provide ample protein.
Key Takeaways:
Protein is essential for cell repair, growth, and development.
Both animal and plant sources offer adequate protein for a balanced diet.
Lean meats, fish, eggs, legumes, nuts, and seeds are good sources of protein.
The daily recommended intake of protein is 10% to 35% of total calorie needs.
Consult a registered health care professional for personalized dietary guidance.
The Importance of Protein for Growth and Development
Protein is an essential nutrient that plays a crucial role in supporting growth and development, particularly in children, teens, and pregnant women. During these periods of life, the body requires ample amounts of protein to fuel the growth and repair of tissues.
It is composed of amino acids, some of which are produced by the body and others that must be obtained from food sources. These essential amino acids are particularly vital during periods of rapid growth and development, as they contribute to the formation of new cells, tissues, and organs.
It is important to incorporate a balanced of protein into the daily diet to support optimal growth and development. Rather than consuming all the protein in one meal, it is recommended to distribute protein intake evenly throughout the day. This ensures a steady supply of essential amino acids for ongoing bodily functions.
Animal sources of protein, such as lean meats, milk, fish, and eggs, are rich in essential amino acids, making them excellent options for meeting protein requirements. However, plant sources like soy, beans, legumes, and certain grains can also provide adequate protein and are suitable for those following a vegetarian or vegan diet.
By ensuring a sufficient intake of protein, individuals can support their growth and development, promote tissue repair, and provide the body with the necessary building blocks for optimal health.
Key Takeaways:
Protein is crucial for growth and development, especially in children, teens, and pregnant women.
Essential amino acids obtained from protein-rich foods support the formation of new cells and tissues.
Distribute high protein intake evenly throughout the day to maintain a steady supply of essential amino acids.
Animal and plant-based protein sources can provide adequate protein for growth and development.
The recommended of protein depends on individual calorie needs.
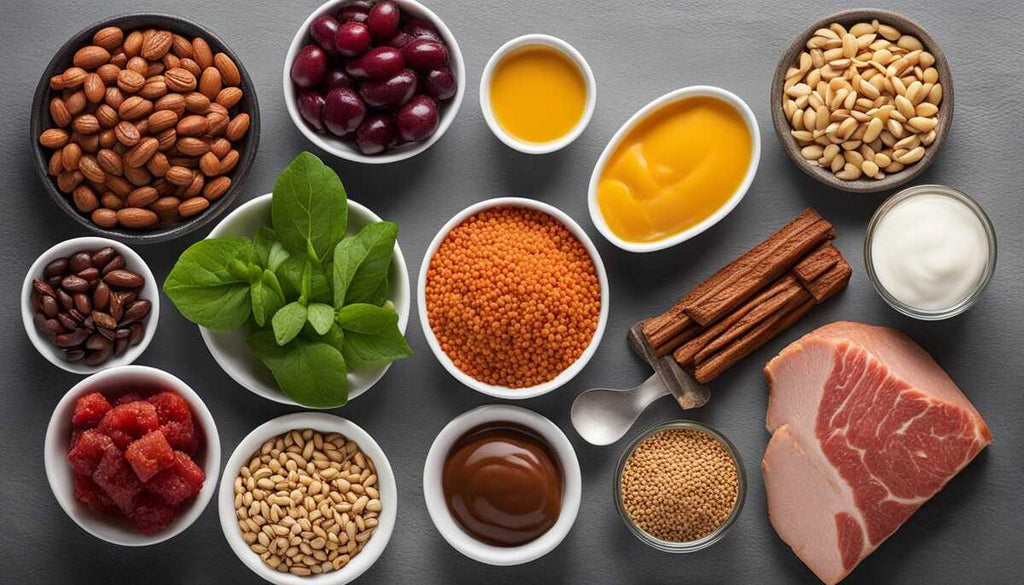
Protein Sources for a Balanced Diet
When it comes to maintaining a balanced diet, incorporating a variety of protein sources is essential. Whether you follow a vegetarian, vegan, or omnivorous lifestyle, there are numerous options to choose from.
Animal Sources
If you prefer animal-based proteins, there are several choices to consider:
Poultry, such as chicken and turkey
Lean cuts of beef or pork
Fatty fish, like salmon or trout, which are also rich in omega-3 fatty acids
Shellfish, including shrimp, crab, and lobster
Plant-Based Protein Sources
For those embracing a plant-based diet, there's a plethora of options brimming with protein:
Beans: Black beans, chickpeas, and kidney beans are protein-packed staples.
Lentils: High in both protein and fiber, lentils are a nutritious choice.
Tofu: This versatile soy-based protein can be prepared in countless ways to suit any dish.
Tempeh: With a nutty flavor, tempeh offers a protein boost as a fermented soy product.
Nuts: Almonds, walnuts, and peanuts provide protein but remember, they're also high in fat, so watch your portions.
Seeds: Chia seeds, flaxseeds, and hemp seeds are excellent protein sources, rich in essential nutrients.
While nuts and seeds are beneficial for protein intake, their fat content necessitates mindful portion control for a balanced diet.
Additionally, whole grains like quinoa, brown rice, and whole wheat bread also contain protein and can be incorporated into meals for added nutrition.
For reference, the US Department of Agriculture's MyPlate guide provides valuable recommendations for making healthy food choices, including protein-rich options.
Protein Source Protein Content per 100g Calories per 100g
Chicken Breast 31g 165
Salmon 20g 206
Lentils 9g 116
Tofu 8g 144
Almonds 21g 579
Quinoa 4g 120
The Crucial Importance of Protein in Your Body
Protein plays a significant role in various functions of the body. It is an essential nutrient that serves as the building blocks for bones, muscles, cartilage, and skin. Without an adequate daily protein intake, the body's ability to repair and maintain these vital tissues would be compromised.
Moreover, protein is involved in carrying oxygen throughout the body via red blood cells. Hemoglobin, a protein found in red blood cells, binds to oxygen in the lungs and transports it to tissues and organs, enabling them to function optimally.
Enzymes, another type of protein, are responsible for facilitating digestion. These enzymes break down food into smaller molecules, allowing the body to absorb and utilize essential nutrients effectively. Without protein, the digestive process would be hindered, leading to nutrient deficiencies and potential health complications.
Protein also plays a crucial role in hormone regulation, particularly during puberty when significant changes in the body occur. Hormones act as messengers, controlling various bodily functions such as growth, metabolism, and reproduction. Protein is necessary for the production and regulation of these hormones, ensuring their proper function.
In adition to these fundamental functions, protein has various other benefits. It aids in the recovery and repair of tissues after exercise or injury, minimizing muscle loss and promoting the growth of lean muscle mass. It also contributes to maintaining a healthy weight by enhancing satiety and curbing hunger, reducing the likelihood of overeating.
Overall, a balanced diet rich in protein is essential for optimal body functions and overall well-being. By including protein-rich foods in your meals, you provide your body with the necessary nutrients to support its various functions and maintain good health.
The Benefits of Protein in Your Body Functions:
Supports tissue repair and maintenance
Aids in carrying oxygen throughout the body
Facilitates digestion through enzyme production
Regulates hormones, especially during puberty
Promotes recovery after exercise or injury
Reduces muscle loss and builds lean muscle mass
Maintains a healthy weight by curbing hunger
"Protein is essential for the proper functioning of our body, supporting everything from tissue repair to hormone regulation." - Dr. Sarah Johnson, Nutritionist
Balanced Diet: Harnessing Protein for Optimal Health and Energy
Consuming enough protein is crucial for maintaining optimal health and energy levels. Protein plays a fundamental role in the creation and maintenance of every cell in our bodies, making it an essential nutrient for overall well-being. It helps fuel our cells, providing the energy necessary to carry out various bodily functions. By including protein in our daily nutrition, we support proper cell function and promote overall health maintenance.
it contributes to the production of neurotransmitters, which are essential for brain function and productivity. By providing the building blocks for neurotransmitters, protein helps improve mental clarity and cognitive function.
When it comes to weight management, protein plays a vital role in curbing hunger and promoting satiety. When we consume protein-rich foods, they take longer to digest, keeping us full for longer periods. This can prevent excessive calorie intake and aid in weight control.
The Power of Protein and Fiber: Fulfilling Important Functions for Your Health
Incorporating protein into a balanced diet, along with fiber, can be particularly beneficial for overall health and weight management. Both protein and fiber slow down digestion, helping regulate blood sugar levels and preventing energy crashes throughout the day.
Protein-rich foods help stabilize blood sugar levels by slowing down the absorption of glucose into the bloodstream. This steady release of energy can improve focus and concentration, supporting productivity and mental performance.
"Combining protein and fiber in your meals can help maintain steady energy levels and keep you feeling satisfied throughout the day." - Dr. Meera Patel, Dietician
To harness the power of protein and fiber, include nutrient-dense foods such as lean meats, fish, eggs, legumes, whole grains, fruits, and vegetables in your daily diet.
Here is a comparative table showcasing the protein content of common animal and plant-based sources:
Protein Sources Protein Content (per 100g)
Chicken Breast 31g
Salmon 26g
Greek Yogurt 10g
Chickpeas 19g
Lentils 9g
Quinoa 4g
Remember to consult with a registered healthcare professional or nutritionist to determine the proper protein intake based on your individual needs and health goals.
Reasons to Eat More Protein: Elevating Your Diet for Optimal Health
Introduction: Protein is often regarded as the cornerstone of a balanced diet, and for good reason. It serves as a vital nutrient with numerous benefits for your health and well-being. Let's explore some compelling reasons why incorporating more protein into your diet can be advantageous.
Supports Muscle Growth and Repair: Protein is essential for building and repairing muscle tissues, making it indispensable for individuals aiming to enhance muscle strength and endurance, as well as those recovering from injuries or intense workouts.
Aids in Weight Management: Protein has a satiating effect, helping you feel fuller for longer periods and reducing overall calorie intake. By including protein-rich foods in your meals, you may experience fewer cravings and find it easier to maintain a healthy weight.
Promotes Bone Health: Protein is not only crucial for muscles but also plays a role in maintaining strong and healthy bones. Adequate protein intake may helps preserve bone density and reduces the risk of osteoporosis and fractures, especially as you age.
Balances Blood Sugar Levels: Including protein in your meals helps stabilize blood sugar levels by slowing down the absorption of carbohydrates. This can prevent spikes and crashes in blood sugar, reducing the risk of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes.
Supports Immune Function: Protein is involved in the production of antibodies and immune cells, helping to strengthen the body's immune system and defend against infections and diseases.
Enhances Mood and Mental Health: Protein-rich foods contain amino acids that are precursors to neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine, which play a role in regulating mood and mental well-being. Consuming adequate protein may help improve mood and alleviate symptoms of depression and anxiety.
Preserves Lean Body Mass During Weight Loss: When you're trying to lose weight, preserving lean body mass is essential to ensure that the weight lost comes from fat stores rather than muscle tissue. Adequate protein intake helps maintain muscle mass during calorie restriction, supporting long-term weight loss success.
Conclusion
Incorporating protein into a balanced daily diet is crucial for maintaining overall health and well-being. A balanced diet should include a variety of protein sources, both animal and plant-based, to meet the recommended daily intake. Protein plays a vital role in supporting growth and development, aiding in body functions, and providing energy.
When combined with other nutritious foods, a balanced diet can contribute to weight management and overall nutrition. Protein, along with fiber, helps promote a feeling of fullness and satiety, preventing excessive calorie intake and aiding in weight management. It is important to note that individual dietary needs may vary, and consulting a registered healthcare professional can provide personalized guidance.
By prioritizing a balanced diet and incorporating protein-rich foods, individuals can support their overall health goals, maintain a healthy weight, and ensure optimal nutrition. Remember, making healthy food choices and embracing a balanced approach to eating are key to achieving a well-rounded, sustainable lifestyle.
FAQ
Why is protein important in a balanced daily diet?
Protein is essential for cell repair, growth, and development. It plays a vital role in maintaining good health and can be obtained from both animal and plant sources.
How much protein do healthy adults need to consume?
The daily recommended intake of protein for healthy adults is 10% to 35% of total calorie needs. It is recommended to consume a balanced of protein throughout the day rather than at every meal.
What is the role of amino acids in the body?
Amino acids play a variety of roles in the body, including serving as the building blocks of proteins, supporting muscle growth and repair, regulating immune function, contributing to neurotransmitter synthesis, and facilitating metabolic processes.
What role does protein play in the body?
Protein is essential for building and repairing bones, muscles, cartilage, and skin. It helps carry oxygen throughout the body, aids in digestion, and regulates hormones. Protein can also assist in recovery after exercise or injury, reduce muscle loss, build lean muscle, maintain a healthy weight, and curb hunger.
Why is consuming enough protein important for overall health?
Consuming enough protein is crucial for maintaining optimal health and energy levels. Protein is involved in the creation and maintenance of every cell in our bodies and helps fuel our cells for energy.
What are the long-term effects of protein deficiency?
Long-term protein deficiency can lead to muscle wasting, impaired immune function, delayed wound healing, stunted growth in children, and a higher risk of infections and chronic diseases.